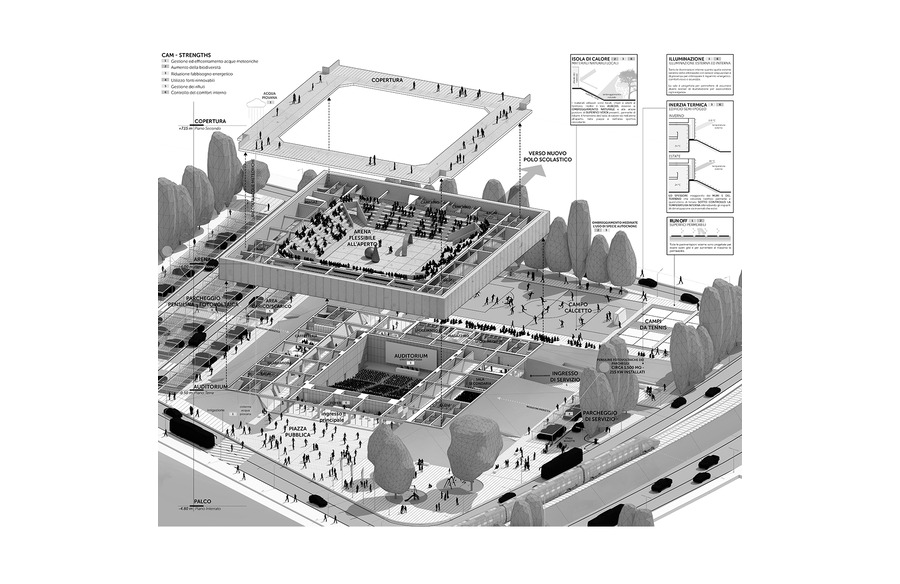
Elastic Ice A Breakthrough in Material Science

Introduction to Elastic Ice
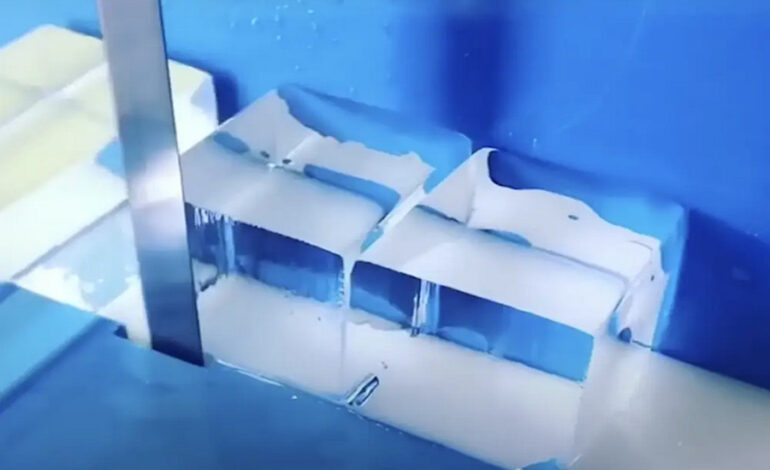
In a remarkable breakthrough, Chinese researchers have developed flexible ice microfibers that can bend and curl like wires. This innovation holds immense potential for various applications, including light transmission similar to fiber optics. The process involves cooling water vapor with liquid nitrogen to form microfibers, as described in a research article published in Science.
Elastic Properties of Ice Microfibers
Unlike traditional ice, which is brittle, these elastic ice microfibers exhibit remarkable flexibility when subjected to pressure. The researchers achieved this by electrifying a tungsten pin inside a chamber cooled with liquid nitrogen, causing water vapor to condense and form the microfibers. At extremely low temperatures, the ice microfibers demonstrated elastic properties, bending up to a maximum deformation of 10.9%, compared to 0.3% for normal ice.
Potential Applications
The transparency of these microfibers opens up possibilities for light transmission, making them suitable for applications akin to fiber-optic cables. Moreover, the researchers envision using the ice microfibers to create tiny sensors capable of detecting air pollution. Particles such as soot can adhere to the ice, facilitating the collection of data on the quantity and composition of pollutants in a given area.
Future Implications
The development of flexible ice fibers represents a significant advancement in material science, offering opportunities for exploring ice physics and related technologies at micro- and nanometer scales. This innovation underscores the ongoing evolution in materials research, with implications for various fields, including environmental monitoring and telecommunications.
Conclusion
The creation of elastic ice microfibers marks a significant milestone in material science, showcasing the potential for novel solutions in diverse applications. As researchers continue to explore the properties and applications of these innovative materials, they pave the way for advancements that could address pressing challenges and drive innovation across industries.